Table of Contents
入手准备 Link to 入手准备
首先,确保Linux上安装了gdb:
12sudo apt update
sudo apt-get install gdb
在bomb.c文件中的是main()函数,这里截取主要部分,看到程序逻辑:
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142434445464748495051525354555657585960616263646566#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "support.h"
#include "phases.h"
/* * Note to self: Remember to erase this file so my victims will have no
* idea what is going on, and so they will all blow up in a
* spectaculary fiendish explosion. -- Dr. Evil */
FILE *infile;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char *input;
// 这里略去输入重定向的处理...
/* Do all sorts of secret stuff that makes the bomb harder to defuse. */
initialize_bomb();
printf("Welcome to my fiendish little bomb. You have 6 phases with\n");
printf("which to blow yourself up. Have a nice day!\n");
/* Hmm... Six phases must be more secure than one phase! */
input = read_line(); /* Get input */
phase_1(input); /* Run the phase */
phase_defused(); /* Drat! They figured it out!
* Let me know how they did it. */
printf("Phase 1 defused. How about the next one?\n");
/* The second phase is harder. No one will ever figure out
* how to defuse this... */
input = read_line();
phase_2(input);
phase_defused();
printf("That's number 2. Keep going!\n");
/* I guess this is too easy so far. Some more complex code will
* confuse people. */
input = read_line();
phase_3(input);
phase_defused();
printf("Halfway there!\n");
/* Oh yeah? Well, how good is your math? Try on this saucy problem! */
input = read_line();
phase_4(input);
phase_defused();
printf("So you got that one. Try this one.\n");
/* Round and 'round in memory we go, where we stop, the bomb blows! */
input = read_line();
phase_5(input);
phase_defused();
printf("Good work! On to the next...\n");
/* This phase will never be used, since no one will get past the
* earlier ones. But just in case, make this one extra hard. */
input = read_line();
phase_6(input);
phase_defused();
/* Wow, they got it! But isn't something... missing? Perhaps
* something they overlooked? Mua ha ha ha ha! */
return 0;
显然,解谜要点隐藏在phase_1, phase_2,…, phase_6中
1gdb bomb
设置断点,阻止炸弹爆炸:
1(gdb) b explode_bomb
这是explode_bomb代码,不再深究:
12345678910(gdb) disassemble explode_bomb
Dump of assembler code for function explode_bomb:
0x000000000040143a <+0>: sub $0x8,%rsp
0x000000000040143e <+4>: mov $0x4025a3,%edi
0x0000000000401443 <+9>: call 0x400b10 <puts@plt>
0x0000000000401448 <+14>: mov $0x4025ac,%edi
0x000000000040144d <+19>: call 0x400b10 <puts@plt>
0x0000000000401452 <+24>: mov $0x8,%edi
0x0000000000401457 <+29>: call 0x400c20 <exit@plt>
End of assembler dump.
运行程序:
1(gdb)r
phase_1 Link to phase_1
在gdb中使用反汇编工具
1(gdb)disasemble phase_1
得到反汇编结果:
12345678910Dump of assembler code for function phase_1:
0x00400ee0 <+0>: sub $0x8,%rsp
0x00400ee4 <+4>: mov $0x402400,%esi
0x00400ee9 <+9>: call 0x401338 <strings_not_equal>
0x00400eee <+14>: test %eax,%eax
0x00400ef0 <+16>: je 0x400ef7 <phase_1+23>
0x00400ef2 <+18>: call 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x00400ef7 <+23>: add $0x8,%rsp
0x00400efb <+27>: ret
End of assembler dump.
注意到 test %eax, %eax,当%eax=0的时候会执行 je,跳过explor_bomb函数,解开炸弹 %esi的值是0x00402400(32bits) 看到有一个<strings_not_equal>函数,继续
1(gdb) disassemble strings_not_equal
得到
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738394041Dump of assembler code for function strings_not_equal:
0x00401338 <+0>: push %r12
0x0040133a <+2>: push %rbp
0x0040133b <+3>: push %rbx
0x0040133c <+4>: mov %rdi,%rbx # %rdi是存放input指针,先复制到%rbx
0x0040133f <+7>: mov %rsi,%rbp # %rbp复制为0x402400
0x00401342 <+10>: call 0x40131b <string_length>
0x00401347 <+15>: mov %eax,%r12d # input字符串的长度存放到%r12d
0x0040134a <+18>: mov %rbp,%rdi # 把%rbp赋值给函数参数%rdi
0x0040134d <+21>: call 0x40131b <string_length> # 返回%rdi的长度
0x00401352 <+26>: mov $0x1,%edx # %edx赋值为1
0x00401357 <+31>: cmp %eax,%r12d # 0x402400字符串的长度与input字符串长度相比较
0x0040135a <+34>: jne 0x40139b <strings_not_equal+99> # 必须相等,否则函数将返回1
0x0040135c <+36>: movzbl (%rbx),%eax
0x0040135f <+39>: test %al,%al
0x00401361 <+41>: je 0x401388 <strings_not_equal+80>
0x00401363 <+43>: cmp 0x0(%rbp),%al
0x00401366 <+46>: je 0x401372 <strings_not_equal+58>
0x00401368 <+48>: jmp 0x40138f <strings_not_equal+87>
--Type <RET> for more, q to quit, c to continue without paging--c
0x0040136a <+50>: cmp 0x0(%rbp),%al
0x0040136d <+53>: nopl (%rax)
0x00401370 <+56>: jne 0x401396 <strings_not_equal+94>
0x00401372 <+58>: add $0x1,%rbx
0x00401376 <+62>: add $0x1,%rbp
0x0040137a <+66>: movzbl (%rbx),%eax
0x0040137d <+69>: test %al,%al
0x0040137f <+71>: jne 0x40136a <strings_not_equal+50>
0x00401381 <+73>: mov $0x0,%edx
0x00401386 <+78>: jmp 0x40139b <strings_not_equal+99>
0x00401388 <+80>: mov $0x0,%edx
0x0040138d <+85>: jmp 0x40139b <strings_not_equal+99>
0x0040138f <+87>: mov $0x1,%edx
0x00401394 <+92>: jmp 0x40139b <strings_not_equal+99>
0x00401396 <+94>: mov $0x1,%edx
0x0040139b <+99>: mov %edx,%eax
0x0040139d <+101>: pop %rbx
0x0040139e <+102>: pop %rbp
0x0040139f <+103>: pop %r12
0x004013a1 <+105>: ret
End of assembler dump.
看到有一个<string_length>函数,继续
1(gdb) disassemble string_length
得到
12345678910111213Dump of assembler code for function string_length:
0x0040131b <+0>: cmpb $0x0,(%rdi)
0x0040131e <+3>: je 0x401332 <string_length+23>
0x00401320 <+5>: mov %rdi,%rdx
0x00401323 <+8>: add $0x1,%rdx
0x00401327 <+12>: mov %edx,%eax
0x00401329 <+14>: sub %edi,%eax
0x0040132b <+16>: cmpb $0x0,(%rdx)
0x0040132e <+19>: jne 0x401323 <string_length+8>
0x00401330 <+21>: repz ret
0x00401332 <+23>: mov $0x0,%eax
0x00401337 <+28>: ret
End of assembler dump.
这是一个简单的函数,返回%rdi指向的字符串的长度到%eax 一步一步看下来,感觉是逐个比较输入字符串与0x402400字符串,相同就拆除了炸弹.
12(gdb) x /s 0x402400
0x402400: "Border relations with Canada have never been better."
就可以显示该地址对应的字符串. 拆开第一个炸弹的结果:
123456789(gdb) r
Starting program: /mnt/e/Documents/C/CSAPP/bomb/bomb
[Thread debugging using libthread_db enabled]
Using host libthread_db library "/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libthread_db.so.1".
Welcome to my fiendish little bomb. You have 6 phases with
which to blow yourself up. Have a nice day!
Border relations with Canada have never been better.
Phase 1 defused. How about the next one?
phase_2 Link to phase_2
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829(gdb) disassemble phase_2
Dump of assembler code for function phase_2:
0x00400efc <+0>: push %rbp
0x00400efd <+1>: push %rbx
0x00400efe <+2>: sub $0x28,%rsp # 栈顶指针减去0x28(40)
0x00400f02 <+6>: mov %rsp,%rsi # 此时复制给%rsi
0x00400f05 <+9>: call 0x40145c <read_six_numbers>
0x00400f0a <+14>: cmpl $0x1,(%rsp) # %rsp指向的内存的值应该是0x1
0x00400f0e <+18>: je 0x400f30 <phase_2+52> # 去52看看
0x00400f10 <+20>: call 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x00400f15 <+25>: jmp 0x400f30 <phase_2+52>
0x00400f17 <+27>: mov -0x4(%rbx),%eax # %rbx-4=%rsp,%rsp指向的内存的值赋值给%eax
0x00400f1a <+30>: add %eax,%eax # %eax的值乘以2
0x00400f1c <+32>: cmp %eax,(%rbx) # 比较%eax和%rbx=%rcx指向的内存的值
0x00400f1e <+34>: je 0x400f25 <phase_2+41> # 必须相等,去41看看
0x00400f20 <+36>: call 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x00400f25 <+41>: add $0x4,%rbx # %rbx=%rbx+4=%r8
0x00400f29 <+45>: cmp %rbp,%rbx
0x00400f2c <+48>: jne 0x400f17 <phase_2+27>
0x00400f2e <+50>: jmp 0x400f3c <phase_2+64>
--Type <RET> for more, q to quit, c to continue without paging--c
0x00400f30 <+52>: lea 0x4(%rsp),%rbx # 此时%rcx=%rbx
0x00400f35 <+57>: lea 0x18(%rsp),%rbp # 底部加上24的地址记为%rbp
0x00400f3a <+62>: jmp 0x400f17 <phase_2+27> # 去27看看
0x00400f3c <+64>: add $0x28,%rsp
0x00400f40 <+68>: pop %rbx
0x00400f41 <+69>: pop %rbp
0x00400f42 <+70>: ret
End of assembler dump.
1234567891011121314151617181920(gdb) disassemble read_six_numbers
Dump of assembler code for function read_six_numbers:
0x000000000040145c <+0>: sub $0x18,%rsp # 栈顶指针再减去0x18(24)
0x0000000000401460 <+4>: mov %rsi,%rdx # 底部是%rsp,顶部是%rsi,复制给%rdx
0x0000000000401463 <+7>: lea 0x4(%rsi),%rcx # 顶部加上4的地址记为%rcx
0x0000000000401467 <+11>: lea 0x14(%rsi),%rax # 顶部加上20的地址记为%rax
0x000000000040146b <+15>: mov %rax,0x8(%rsp) # %rsp+8那块内存保存了%rax
0x0000000000401470 <+20>: lea 0x10(%rsi),%rax # 顶部加上16的地址记为%rax
0x0000000000401474 <+24>: mov %rax,(%rsp) # 底部那块内存保存了%rax
0x0000000000401478 <+28>: lea 0xc(%rsi),%r9 # 顶部加上12的地址记为%r9
0x000000000040147c <+32>: lea 0x8(%rsi),%r8 # 顶部加上8的地址记为%r8
0x0000000000401480 <+36>: mov $0x4025c3,%esi # %esi赋值为0x4025c3,我们可以打印这个内存地址的内容
0x0000000000401485 <+41>: mov $0x0,%eax # %eax赋值为0
0x000000000040148a <+46>: call 0x400bf0 <__isoc99_sscanf@plt> # 我说怎么没用到%rdi呢,原来在这里处理输入
0x000000000040148f <+51>: cmp $0x5,%eax # sscanf函数的返回值与5相比较
0x0000000000401492 <+54>: jg 0x401499 <read_six_numbers+61>
0x0000000000401494 <+56>: call 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x0000000000401499 <+61>: add $0x18,%rsp # 如果大于5,栈底回到栈顶
0x000000000040149d <+65>: ret
End of assembler dump.
12(gdb) x /s 0x4025c3
0x4025c3: "%d %d %d %d %d %d"
到这里就清晰了,答案应该是6个整数,以空格隔开: 1 2 4 8 16 32 为了避免每次拆炸弹时都要输入一遍之前的答案,bomb.c中告诉我可以带参数运行,能打开文件读取内容.我把这个文件命名为answer
123456789(gdb) r answer
Starting program: /mnt/e/Documents/C/CSAPP/bomb/bomb answer
[Thread debugging using libthread_db enabled]
Using host libthread_db library "/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libthread_db.so.1".
Welcome to my fiendish little bomb. You have 6 phases with
which to blow yourself up. Have a nice day!
Phase 1 defused. How about the next one?
That's number 2. Keep going!
成功了!
phase_3 Link to phase_3
12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031323334353637383940(gdb) disassemble phase_3
Dump of assembler code for function phase_3:
0x0000000000400f43 <+0>: sub $0x18,%rsp # 栈顶指针减去24
0x0000000000400f47 <+4>: lea 0xc(%rsp),%rcx # 栈底+12的地址记为%rcx
0x0000000000400f4c <+9>: lea 0x8(%rsp),%rdx # 栈底+8的地址记为%rdx
0x0000000000400f51 <+14>: mov $0x4025cf,%esi # %esi赋值为0x4025cf
0x0000000000400f56 <+19>: mov $0x0,%eax # %eax赋值为0
0x0000000000400f5b <+24>: call 0x400bf0 <__isoc99_sscanf@plt> # 调用函数
0x0000000000400f60 <+29>: cmp $0x1,%eax # 比较%eax(sscanf函数的返回值)与1
0x0000000000400f63 <+32>: jg 0x400f6a <phase_3+39> # %eax必须大于1,去39看看
0x0000000000400f65 <+34>: call 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x0000000000400f6a <+39>: cmpl $0x7,0x8(%rsp) # 比较%rsp+8与7
0x0000000000400f6f <+44>: ja 0x400fad <phase_3+106> # 负数和大于7的情况:引爆炸弹
0x0000000000400f71 <+46>: mov 0x8(%rsp),%eax # 大于0小于等于7的情况:把%rsp+8指向的内存的值赋值给%eax
0x0000000000400f75 <+50>: jmp *0x402470(,%rax,8) # 跳转到0x402470+%rax*8的地址指向的内存存储的地址处
0x0000000000400f7c <+57>: mov $0xcf,%eax # %rax = 0
0x0000000000400f81 <+62>: jmp 0x400fbe <phase_3+123>
0x0000000000400f83 <+64>: mov $0x2c3,%eax # %rax = 2
0x0000000000400f88 <+69>: jmp 0x400fbe <phase_3+123>
0x0000000000400f8a <+71>: mov $0x100,%eax # %rax = 3
--Type <RET> for more, q to quit, c to continue without paging--c
0x0000000000400f8f <+76>: jmp 0x400fbe <phase_3+123>
0x0000000000400f91 <+78>: mov $0x185,%eax # %rax = 4
0x0000000000400f96 <+83>: jmp 0x400fbe <phase_3+123>
0x0000000000400f98 <+85>: mov $0xce,%eax # %rax = 5
0x0000000000400f9d <+90>: jmp 0x400fbe <phase_3+123>
0x0000000000400f9f <+92>: mov $0x2aa,%eax # %rax = 6
0x0000000000400fa4 <+97>: jmp 0x400fbe <phase_3+123>
0x0000000000400fa6 <+99>: mov $0x147,%eax # %rax = 7
0x0000000000400fab <+104>: jmp 0x400fbe <phase_3+123>
0x0000000000400fad <+106>: call 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x0000000000400fb2 <+111>: mov $0x0,%eax
0x0000000000400fb7 <+116>: jmp 0x400fbe <phase_3+123>
0x0000000000400fb9 <+118>: mov $0x137,%eax # %rax = 1
0x0000000000400fbe <+123>: cmp 0xc(%rsp),%eax # 比较*(%rsp+12)与%eax
0x0000000000400fc2 <+127>: je 0x400fc9 <phase_3+134>
0x0000000000400fc4 <+129>: call 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x0000000000400fc9 <+134>: add $0x18,%rsp
0x0000000000400fcd <+138>: ret
End of assembler dump.
我发现传入sscanf函数总是%esi
12(gdb) x /s 0x4025cf
0x4025cf: "%d %d"
对 0x0000000000400f75 <+50>: jmp *0x402470(,%rax,8) 的理解至关重要.这正是一个跳转表,含义是跳转到0x402470+%rax*8这个地址对应内存的值(也是一个地址). 所以,我打印出0~7所有情况的%rax对应的64位地址:
1234567891011121314151617(gdb) x /8x 0x402470
0x402470: 0x7c 0x0f 0x40 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00
(gdb) x /8x 0x402478
0x402478: 0xb9 0x0f 0x40 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00
(gdb) x /8x 0x402480
0x402480: 0x83 0x0f 0x40 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00
(gdb) x /8x 0x402488
0x402488: 0x8a 0x0f 0x40 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00
(gdb) x /8x 0x402490
0x402490: 0x91 0x0f 0x40 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00
(gdb) x /8x 0x402498
0x402498: 0x98 0x0f 0x40 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00
(gdb) x /8x 0x4024a0
0x4024a0: 0x9f 0x0f 0x40 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00
(gdb) x /8x 0x4024a8
0x4024a8: 0xa6 0x0f 0x40 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00
(gdb)
我已经标注出来. 所以,整个代码的逻辑是,根据输入的第一个整数生成第二个整数(答案),然后比较是否与输入的第二个整数相同.如果相同拆除炸弹,如果不同就爆炸. 答案共有8个:
| num_1d | num_2x | num_2d |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0xcf | 207 |
| 1 | 0x137 | 311 |
| 2 | 0x2c3 | 707 |
| 3 | 0x100 | 256 |
| 4 | 0x185 | 389 |
| 5 | 0xce | 206 |
| 6 | 0x2aa | 682 |
| 7 | 0x147 | 327 |
其中,选用 3 256 是最容易计算的. |
12345678910(gdb) r answer
Starting program: /mnt/e/Documents/C/CSAPP/bomb/bomb answer
[Thread debugging using libthread_db enabled]
Using host libthread_db library "/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libthread_db.so.1".
Welcome to my fiendish little bomb. You have 6 phases with
which to blow yourself up. Have a nice day!
Phase 1 defused. How about the next one?
That's number 2. Keep going!
Halfway there!
成功了!
phase_4 Link to phase_4
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526(gdb) disassemble phase_4
Dump of assembler code for function phase_4:
=> 0x000000000040100c <+0>: sub $0x18,%rsp
0x0000000000401010 <+4>: lea 0xc(%rsp),%rcx # %rcx = %rsp + 12
0x0000000000401015 <+9>: lea 0x8(%rsp),%rdx # %rdx = %rsp + 8
0x000000000040101a <+14>: mov $0x4025cf,%esi
0x000000000040101f <+19>: mov $0x0,%eax
0x0000000000401024 <+24>: call 0x400bf0 <__isoc99_sscanf@plt>
0x0000000000401029 <+29>: cmp $0x2,%eax
0x000000000040102c <+32>: jne 0x401035 <phase_4+41> # 如果输入不是两个量,爆炸
0x000000000040102e <+34>: cmpl $0xe,0x8(%rsp) #
0x0000000000401033 <+39>: jbe 0x40103a <phase_4+46> # *(%rsp+8)<=14
0x0000000000401035 <+41>: call 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x000000000040103a <+46>: mov $0xe,%edx # %edx = 14
0x000000000040103f <+51>: mov $0x0,%esi # %esi = 0
0x0000000000401044 <+56>: mov 0x8(%rsp),%edi # %edi = *(%rsp+8),作为func4的第一个参数
0x0000000000401048 <+60>: call 0x400fce <func4>
0x000000000040104d <+65>: test %eax,%eax
0x000000000040104f <+67>: jne 0x401058 <phase_4+76> # %eax不是0,爆炸
0x0000000000401051 <+69>: cmpl $0x0,0xc(%rsp) # 第二个参数是0
--Type <RET> for more, q to quit, c to continue without paging--c
0x0000000000401056 <+74>: je 0x40105d <phase_4+81> # *(%rsp+12)==0
0x0000000000401058 <+76>: call 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x000000000040105d <+81>: add $0x18,%rsp
0x0000000000401061 <+85>: ret
End of assembler dump.
依照套路,查看0x4025cf
12(gdb) x /s 0x4025cf
0x4025cf: "%d %d"
跟phase_3用的是同一个,sscanf接收两个整数输入.
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526(gdb) disassemble func4
Dump of assembler code for function func4:
0x0000000000400fce <+0>: sub $0x8,%rsp
0x0000000000400fd2 <+4>: mov %edx,%eax # %eax = 14
0x0000000000400fd4 <+6>: sub %esi,%eax # %eax -= 0
0x0000000000400fd6 <+8>: mov %eax,%ecx # %ecx = %eax
0x0000000000400fd8 <+10>: shr $0x1f,%ecx # %ecx = %ecx的最高位(逻辑右移31位)
0x0000000000400fdb <+13>: add %ecx,%eax # %eax += %ecx
0x0000000000400fdd <+15>: sar %eax # %eax算术右移1位=7
0x0000000000400fdf <+17>: lea (%rax,%rsi,1),%ecx # %ecx = %rax + %rsi=7
0x0000000000400fe2 <+20>: cmp %edi,%ecx
0x0000000000400fe4 <+22>: jle 0x400ff2 <func4+36> # 如果%ecx<=%edi
0x0000000000400fe6 <+24>: lea -0x1(%rcx),%edx #
0x0000000000400fe9 <+27>: call 0x400fce <func4>
0x0000000000400fee <+32>: add %eax,%eax
0x0000000000400ff0 <+34>: jmp 0x401007 <func4+57>
0x0000000000400ff2 <+36>: mov $0x0,%eax
0x0000000000400ff7 <+41>: cmp %edi,%ecx
0x0000000000400ff9 <+43>: jge 0x401007 <func4+57>
0x0000000000400ffb <+45>: lea 0x1(%rcx),%esi
--Type <RET> for more, q to quit, c to continue without paging--c
0x0000000000400ffe <+48>: call 0x400fce <func4>
0x0000000000401003 <+53>: lea 0x1(%rax,%rax,1),%eax
0x0000000000401007 <+57>: add $0x8,%rsp
0x000000000040100b <+61>: ret
End of assembler dump.
实在太混乱了,我只好学习如何单步执行汇编代码: 在gdb中,
12345678910b explode_bomb
b phase_4
set diassamble-next-line on
layout regs
r answer
si
si
...
ni
...
这是执行 4 5后首次来到fun4函数的界面,%eax和%edx初始化为14 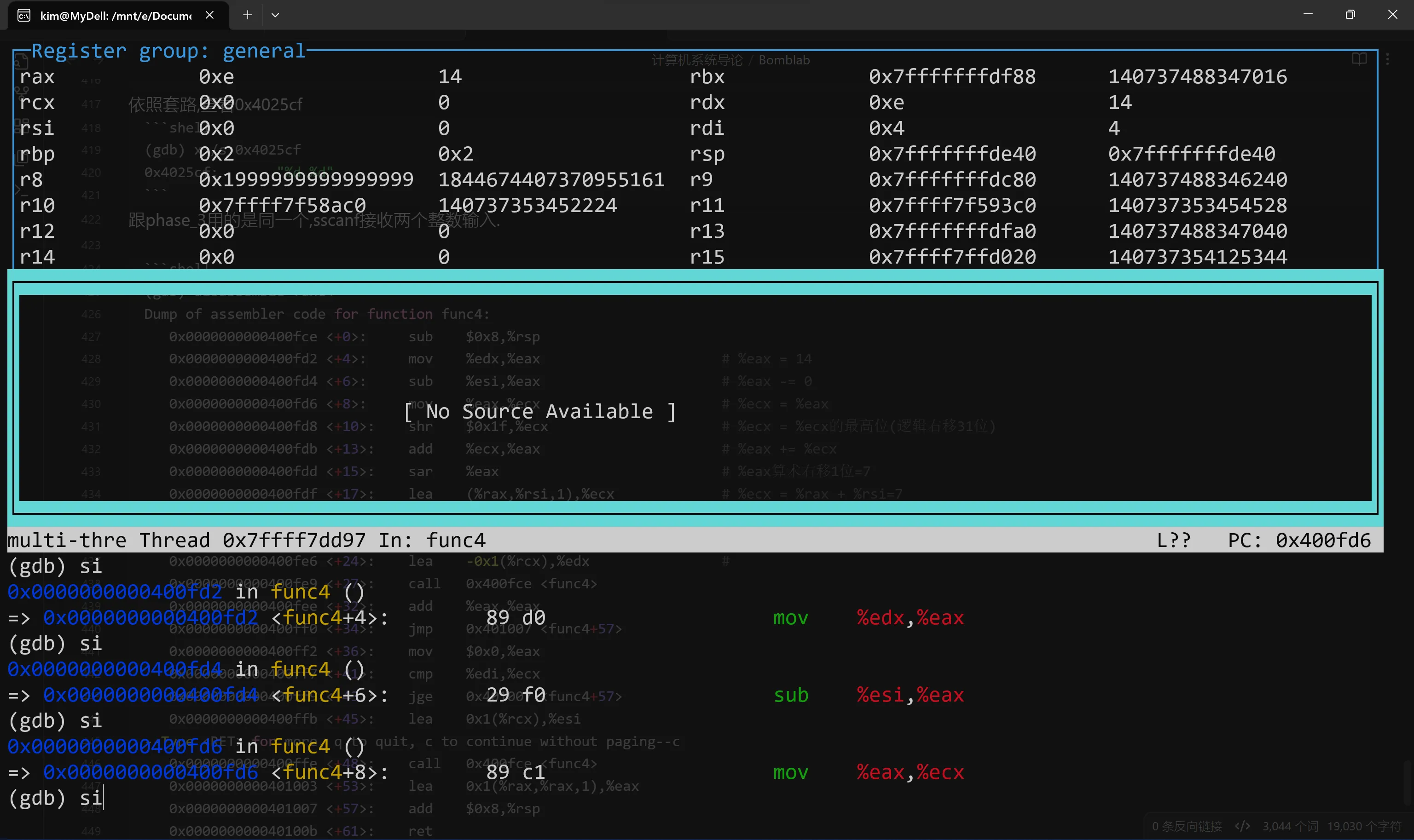 %eax右移得到7
%eax右移得到7 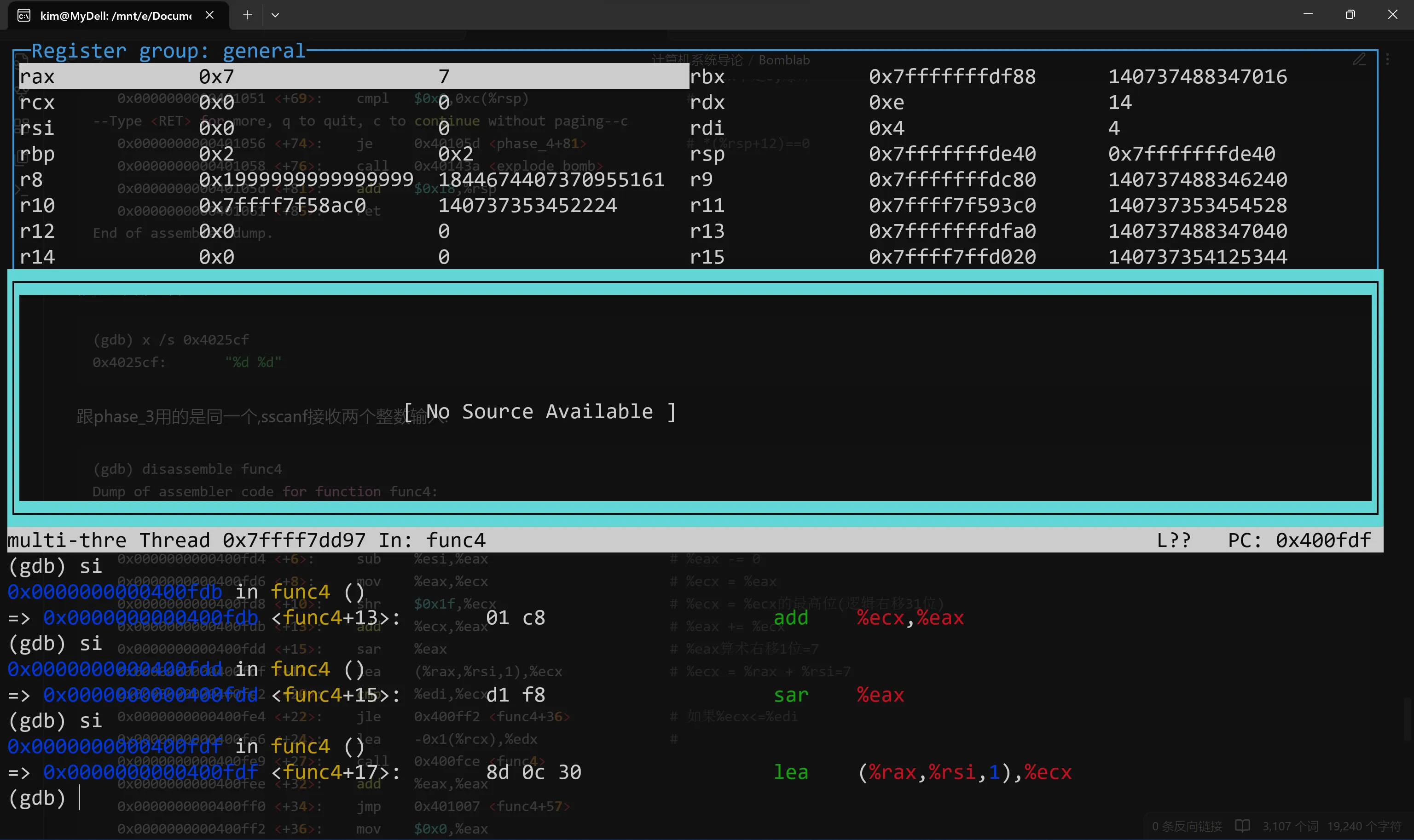 把我输入的第一个参数与7比较,发现7>4,现在%edx变为%ecx-1=6
把我输入的第一个参数与7比较,发现7>4,现在%edx变为%ecx-1=6 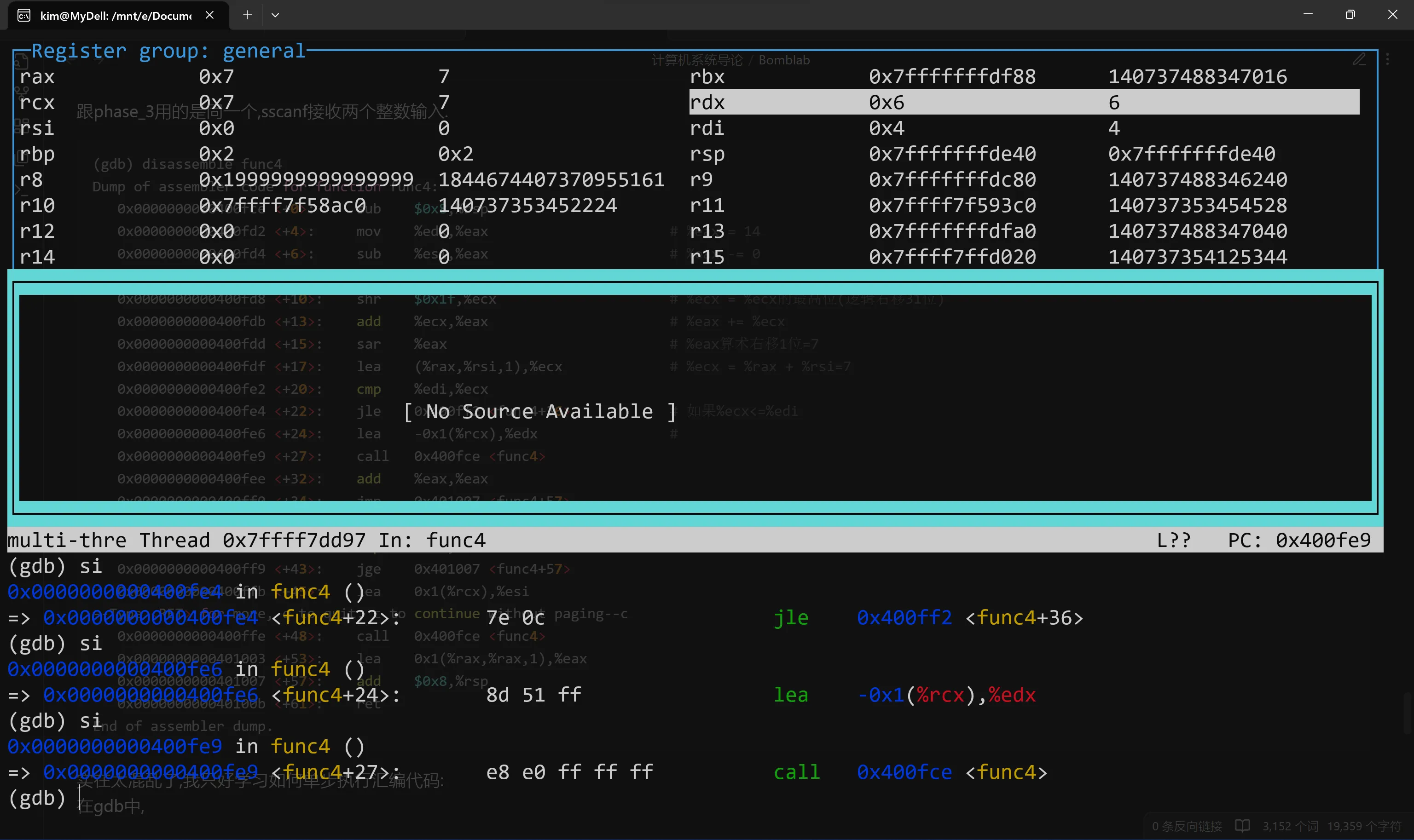 并且进入了函数嵌套.回到这一步,现在3<=4,%eax设置为0
并且进入了函数嵌套.回到这一步,现在3<=4,%eax设置为0 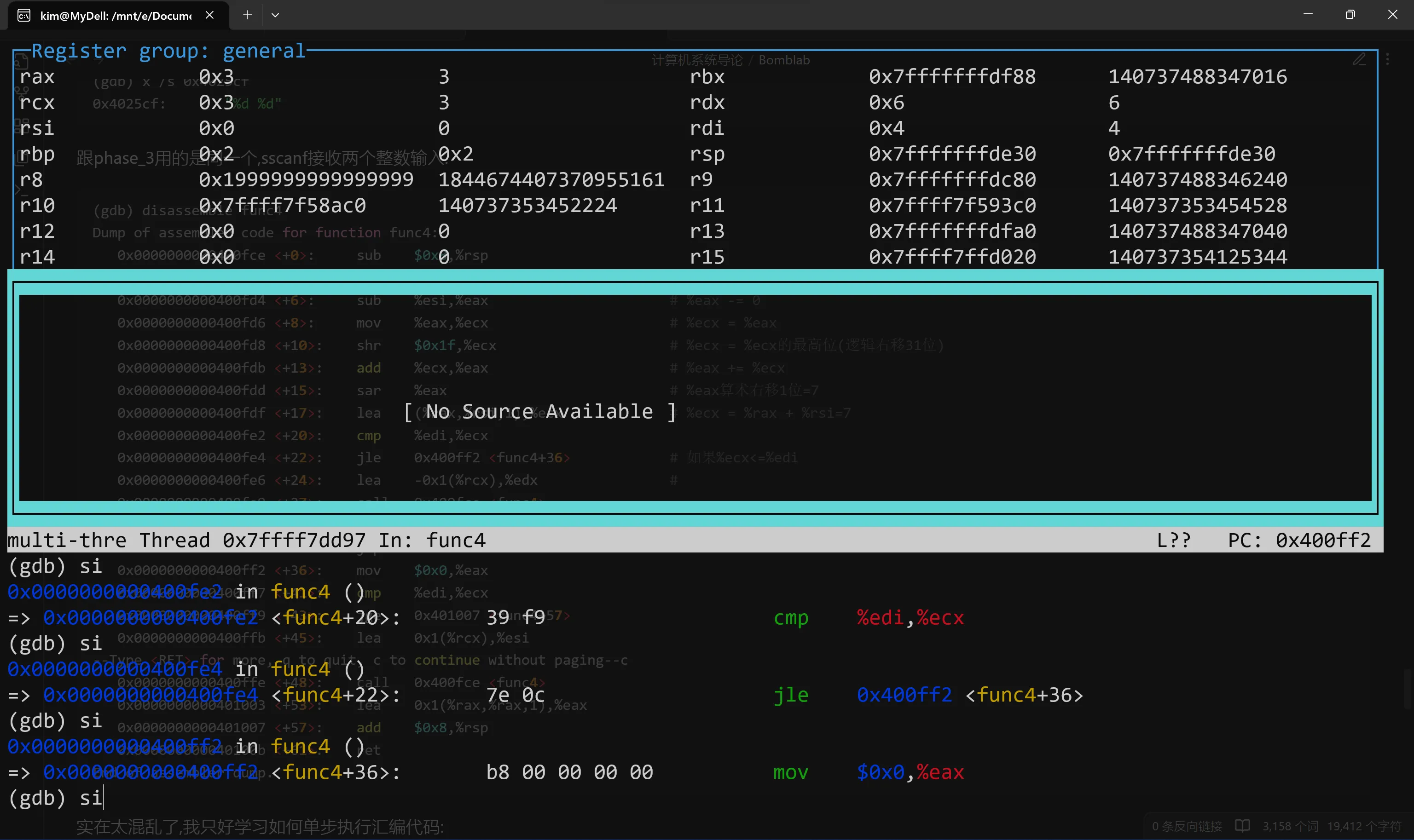 发现4>3,又进入函数嵌套 现在%eax=(6-4)/2=1,
发现4>3,又进入函数嵌套 现在%eax=(6-4)/2=1, 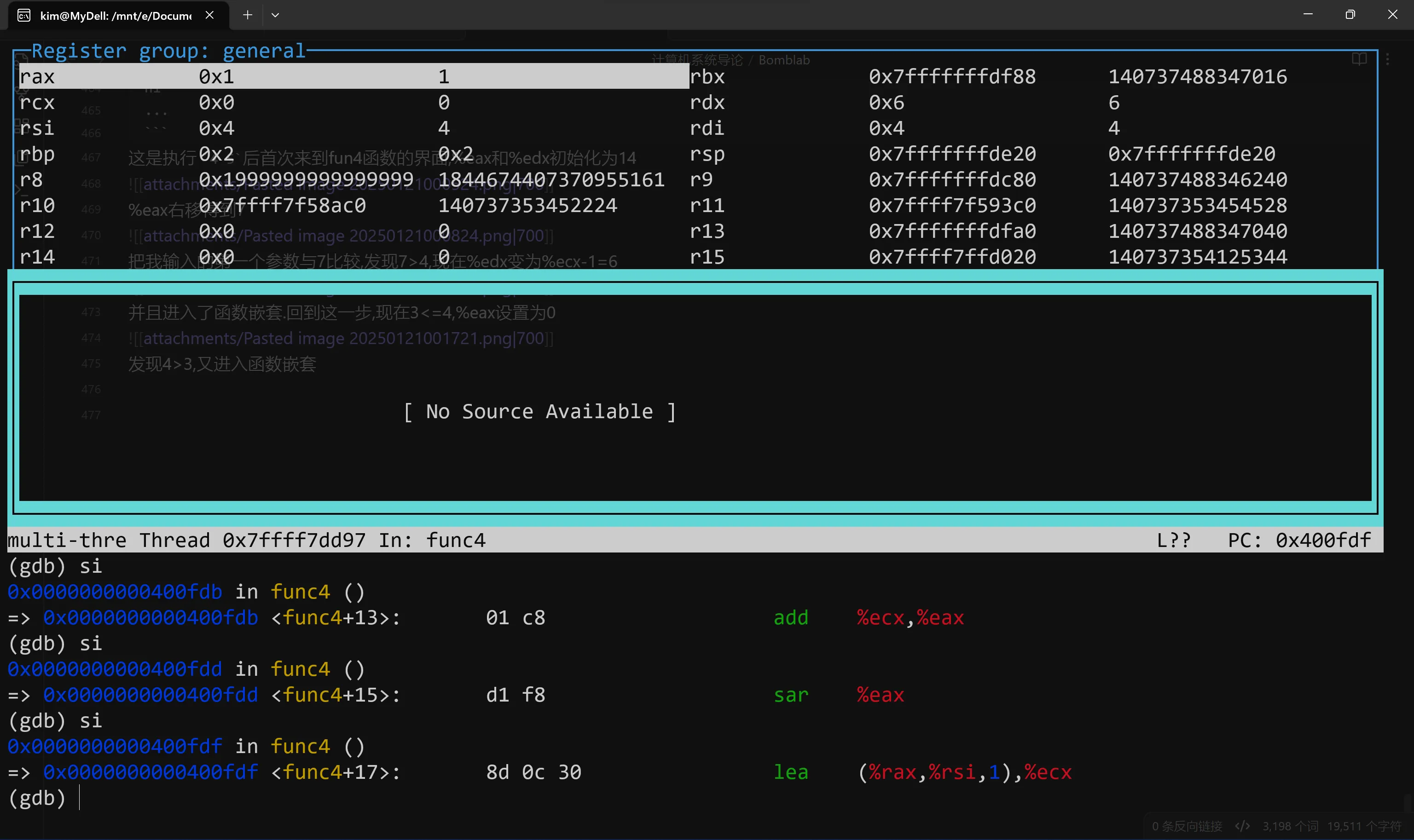
经过这么调试加上这个程序流程图,我大概才明白了这块代码要得到返回0值应该满足7,3,1,0. 
但是对于其他数,它返回值是什么含义呢?好像很混乱,我没有想明白. 至此,我发现了
- 调用函数需要栈顶指针减小,函数返回栈顶指针回去
sscanf函数声明为
1int sscanf(const char *s, const char *format, ... );
这就是format指针用第二个参数%esi传入的原因.
phase_5 Link to phase_5
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142(gdb) disassemble phase_5
Dump of assembler code for function phase_5:
0x0000000000401062 <+0>: push %rbx
0x0000000000401063 <+1>: sub $0x20,%rsp
0x0000000000401067 <+5>: mov %rdi,%rbx
0x000000000040106a <+8>: mov %fs:0x28,%rax
0x0000000000401073 <+17>: mov %rax,0x18(%rsp)
0x0000000000401078 <+22>: xor %eax,%eax
0x000000000040107a <+24>: call 0x40131b <string_length>
0x000000000040107f <+29>: cmp $0x6,%eax # input的string_length是6.
0x0000000000401082 <+32>: je 0x4010d2 <phase_5+112>
0x0000000000401084 <+34>: call 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x0000000000401089 <+39>: jmp 0x4010d2 <phase_5+112>
0x000000000040108b <+41>: movzbl (%rbx,%rax,1),%ecx # 第%rax字符
0x000000000040108f <+45>: mov %cl,(%rsp)
0x0000000000401092 <+48>: mov (%rsp),%rdx
0x0000000000401096 <+52>: and $0xf,%edx # 只取低4位
0x0000000000401099 <+55>: movzbl 0x4024b0(%rdx),%edx # 0x4024b0+这4位的内存的值存储到%edx
0x00000000004010a0 <+62>: mov %dl,0x10(%rsp,%rax,1) #
0x00000000004010a4 <+66>: add $0x1,%rax
0x00000000004010a8 <+70>: cmp $0x6,%rax
0x00000000004010ac <+74>: jne 0x40108b <phase_5+41>
0x00000000004010ae <+76>: movb $0x0,0x16(%rsp)
0x00000000004010b3 <+81>: mov $0x40245e,%esi
0x00000000004010b8 <+86>: lea 0x10(%rsp),%rdi
0x00000000004010bd <+91>: call 0x401338 <strings_not_equal> # 从%rdi开始的字符串与0x401338的字符串比较
0x00000000004010c2 <+96>: test %eax,%eax # 相同返回0
0x00000000004010c4 <+98>: je 0x4010d9 <phase_5+119>
0x00000000004010c6 <+100>: call 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x00000000004010cb <+105>: nopl 0x0(%rax,%rax,1)
--Type <RET> for more, q to quit, c to continue without paging--c
0x00000000004010d0 <+110>: jmp 0x4010d9 <phase_5+119>
0x00000000004010d2 <+112>: mov $0x0,%eax
0x00000000004010d7 <+117>: jmp 0x40108b <phase_5+41>
0x00000000004010d9 <+119>: mov 0x18(%rsp),%rax
0x00000000004010de <+124>: xor %fs:0x28,%rax
0x00000000004010e7 <+133>: je 0x4010ee <phase_5+140>
0x00000000004010e9 <+135>: call 0x400b30 <__stack_chk_fail@plt>
0x00000000004010ee <+140>: add $0x20,%rsp
0x00000000004010f2 <+144>: pop %rbx
0x00000000004010f3 <+145>: ret
End of assembler dump.
这里出现了
12345 0x000000000040106a <+8>: mov %fs:0x28,%rax
0x0000000000401073 <+17>: mov %rax,0x18(%rsp)
...
0x00000000004010de <+124>: xor %fs:0x28,%rax
0x00000000004010e7 <+133>: je 0x4010ee <phase_5+140>
虽然与解开炸弹无关,但经过查阅资料后了解到
为了访问特殊的操作系统数据结构,
FS和GS寄存器都可以用作基准指针地址。因此,您所看到的是从FS寄存器中持有的值加载到偏移量处的值,而不是对FS寄存器内容的位操作。 具体而言,在Linux上的FS:0x28正在存储一个特殊的哨兵堆栈保护值,而代码正在执行堆栈保护检查。例如,如果进一步查看代码,您将看到FS:0x28中的值存储在堆栈上,然后会召回堆栈的内容,并在FS:0x28处使用原始值执行XOR。如果这两个值相等,这意味着由于XOR‘对两个相同的值中的两个值产生零值而设置了零位,那么我们跳到test例程,否则我们跳转到一个特殊的函数,该函数指示堆栈以某种方式损坏,并且存储在堆栈上的前哨值被更改。 首先input的string_length是6.然后循环6此读取输入的字符,从%rsp到%rsp+5,转换后存储到%rsp+0x10到%rsp+0x15,并与0x401338的字符串比较 查看0x401338
12(gdb) x /s 0x40245e
0x40245e: "flyers"
果然是6个字符. 再查看
12(gdb) x /s 0x4024b0
0x4024b0 <array.3449>: "maduiersnfotvbylSo you think you can stop the bomb with ctrl-c, do you?"
由于只有输入的低4位有用,也就是要从前15个字符中寻找”flyers”.依次是 9 15 14 5 6 7 所以有多个答案,只要字符的ASCII码值模16的余数依次是这6个数就行.直接在gdb中打印
12(gdb) printf "%c %c %c %c %c %c",9+64,15+64,14+64,5+64,6+64,7+64
I O N E F G
在answer文件中加上这一行,运行
123456789101112(gdb) r answer
Starting program: /mnt/e/Documents/C/CSAPP/bomb/bomb answer
[Thread debugging using libthread_db enabled]
Using host libthread_db library "/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libthread_db.so.1".
Welcome to my fiendish little bomb. You have 6 phases with
which to blow yourself up. Have a nice day!
Phase 1 defused. How about the next one?
That's number 2. Keep going!
Halfway there!
So you got that one. Try this one.
Good work! On to the next...
成功了!
phase_6 Link to phase_6
来到最后一个!
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142434445464748495051525354555657585960616263646566676869707172737475767778798081828384858687888990(gdb) disassemble phase_6
Dump of assembler code for function phase_6:
0x00000000004010f4 <+0>: push %r14
0x00000000004010f6 <+2>: push %r13
0x00000000004010f8 <+4>: push %r12
0x00000000004010fa <+6>: push %rbp
0x00000000004010fb <+7>: push %rbx
0x00000000004010fc <+8>: sub $0x50,%rsp
0x0000000000401100 <+12>: mov %rsp,%r13
0x0000000000401103 <+15>: mov %rsp,%rsi
0x0000000000401106 <+18>: call 0x40145c <read_six_numbers>
0x000000000040110b <+23>: mov %rsp,%r14
0x000000000040110e <+26>: mov $0x0,%r12d
0x0000000000401114 <+32>: mov %r13,%rbp
0x0000000000401117 <+35>: mov 0x0(%r13),%eax # %r13是%rsp
0x000000000040111b <+39>: sub $0x1,%eax #
0x000000000040111e <+42>: cmp $0x5,%eax
0x0000000000401121 <+45>: jbe 0x401128 <phase_6+52> # %rsp<=6
0x0000000000401123 <+47>: call 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x0000000000401128 <+52>: add $0x1,%r12d # %r12d+=1
0x000000000040112c <+56>: cmp $0x6,%r12d # 1 ~ 5
0x0000000000401130 <+60>: je 0x401153 <phase_6+95> #
0x0000000000401132 <+62>: mov %r12d,%ebx
0x0000000000401135 <+65>: movslq %ebx,%rax
0x0000000000401138 <+68>: mov (%rsp,%rax,4),%eax
0x000000000040113b <+71>: cmp %eax,0x0(%rbp) # 比较第2个到第6个数与第1个数
0x000000000040113e <+74>: jne 0x401145 <phase_6+81> # 不能相等
0x0000000000401140 <+76>: call 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x0000000000401145 <+81>: add $0x1,%ebx
0x0000000000401148 <+84>: cmp $0x5,%ebx
--Type <RET> for more, q to quit, c to continue without paging--c
0x000000000040114b <+87>: jle 0x401135 <phase_6+65>
0x000000000040114d <+89>: add $0x4,%r13
0x0000000000401151 <+93>: jmp 0x401114 <phase_6+32> # 所有6个数字都<=6,并且互不相等,结束以上循环
0x0000000000401153 <+95>: lea 0x18(%rsp),%rsi # %rsi=%rsp+24
0x0000000000401158 <+100>: mov %r14,%rax # %r14=%rsp=%rax
0x000000000040115b <+103>: mov $0x7,%ecx
0x0000000000401160 <+108>: mov %ecx,%edx
0x0000000000401162 <+110>: sub (%rax),%edx # %edx=7-(%rsp第1个整数)
0x0000000000401164 <+112>: mov %edx,(%rax) # 替换
0x0000000000401166 <+114>: add $0x4,%rax # 下一个整数
0x000000000040116a <+118>: cmp %rsi,%rax
0x000000000040116d <+121>: jne 0x401160 <phase_6+108> # 对6个整数都这样操作
0x000000000040116f <+123>: mov $0x0,%esi
0x0000000000401174 <+128>: jmp 0x401197 <phase_6+163>
0x0000000000401176 <+130>: mov 0x8(%rdx),%rdx # %rdx=(%rdx+8) 0x6032d0这是一个链表
0x000000000040117a <+134>: add $0x1,%eax # %eax刚到这里时是1,现在加1是2
0x000000000040117d <+137>: cmp %ecx,%eax # 比较%rax和
0x000000000040117f <+139>: jne 0x401176 <phase_6+130>
0x0000000000401181 <+141>: jmp 0x401188 <phase_6+148>
0x0000000000401183 <+143>: mov $0x6032d0,%edx
0x0000000000401188 <+148>: mov %rdx,0x20(%rsp,%rsi,2) # (%rsp+32/40/...)=0x6032d0
0x000000000040118d <+153>: add $0x4,%rsi
0x0000000000401191 <+157>: cmp $0x18,%rsi # 6次操作
0x0000000000401195 <+161>: je 0x4011ab <phase_6+183> # 6次操作
0x0000000000401197 <+163>: mov (%rsp,%rsi,1),%ecx # 下一个整数
0x000000000040119a <+166>: cmp $0x1,%ecx
0x000000000040119d <+169>: jle 0x401183 <phase_6+143> # 如果一个整数是1,安排链表头指针
0x000000000040119f <+171>: mov $0x1,%eax
0x00000000004011a4 <+176>: mov $0x6032d0,%edx
0x00000000004011a9 <+181>: jmp 0x401176 <phase_6+130> # 我算是看明白了,整数是多少,对应位置就是指向链表第几个元素的地址
0x00000000004011ab <+183>: mov 0x20(%rsp),%rbx # %rbx = 链表[第1个整数]的地址
0x00000000004011b0 <+188>: lea 0x28(%rsp),%rax # %rax= 链表[第二个整数]的地址的地址
0x00000000004011b5 <+193>: lea 0x50(%rsp),%rsi # %rsi = 链表[最后一个整数]的地址的地址
0x00000000004011ba <+198>: mov %rbx,%rcx # %rcx = 链表[第一个整数]的地址
0x00000000004011bd <+201>: mov (%rax),%rdx # %rdx = 链表[第二个整数]的地址
0x00000000004011c0 <+204>: mov %rdx,0x8(%rcx) #
0x00000000004011c4 <+208>: add $0x8,%rax
0x00000000004011c8 <+212>: cmp %rsi,%rax
0x00000000004011cb <+215>: je 0x4011d2 <phase_6+222>
0x00000000004011cd <+217>: mov %rdx,%rcx
0x00000000004011d0 <+220>: jmp 0x4011bd <phase_6+201> # 重新排列了这个链表
0x00000000004011d2 <+222>: movq $0x0,0x8(%rdx) # 尾指针设为0
0x00000000004011da <+230>: mov $0x5,%ebp #
0x00000000004011df <+235>: mov 0x8(%rbx),%rax
0x00000000004011e3 <+239>: mov (%rax),%eax
0x00000000004011e5 <+241>: cmp %eax,(%rbx) # 链表[第1个整数]>=链表[第2个整数]
0x00000000004011e7 <+243>: jge 0x4011ee <phase_6+250>
0x00000000004011e9 <+245>: call 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x00000000004011ee <+250>: mov 0x8(%rbx),%rbx #
0x00000000004011f2 <+254>: sub $0x1,%ebp
0x00000000004011f5 <+257>: jne 0x4011df <phase_6+235> # 要求链表降序排列
0x00000000004011f7 <+259>: add $0x50,%rsp
0x00000000004011fb <+263>: pop %rbx
0x00000000004011fc <+264>: pop %rbp
0x00000000004011fd <+265>: pop %r12
0x00000000004011ff <+267>: pop %r13
0x0000000000401201 <+269>: pop %r14
0x0000000000401203 <+271>: ret
End of assembler dump.
这么啊,太BT了www 哇塞,这些代码虽然很长,但是拆分开来不是很难.逻辑是获取6个输入,要求大于0小于7并且互不相同.依次去内存中一个创建好的链表中寻找对应序列的元素存取在栈上对应的位置(例如第2个输入是3,那么在栈的第2个指针位置放链表第3个元素的指针,此时%rsp+i*8就是”指针的指针”,这里最绕).接着修改链表使其重新排列.最后要求新链表降序排列即可. 我们打印链表(指针部分)
123456789101112(gdb) x /8x 0x6032d8
0x6032d8 <node1+8>: 0xe0 0x32 0x60 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00
(gdb) x /8x 0x6032e8
0x6032e8 <node2+8>: 0xf0 0x32 0x60 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00
(gdb) x /8x 0x6032f8
0x6032f8 <node3+8>: 0x00 0x33 0x60 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00
(gdb) x /8x 0x603308
0x603308 <node4+8>: 0x10 0x33 0x60 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00
(gdb) x /8x 0x603318
0x603318 <node5+8>: 0x20 0x33 0x60 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00
(gdb) x /8x 0x603328
0x603328 <node6+8>: 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00
(数据部分)
123456789101112(gdb) x /8x 0x6032d0
0x6032d0 <node1>: 0x4c 0x01 0x00 0x00 0x01 0x00 0x00 0x00
(gdb) x /8x 0x6032e0
0x6032e0 <node2>: 0xa8 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x02 0x00 0x00 0x00
(gdb) x /8x 0x6032f0
0x6032f0 <node3>: 0x9c 0x03 0x00 0x00 0x03 0x00 0x00 0x00
(gdb) x /8x 0x603300
0x603300 <node4>: 0xb3 0x02 0x00 0x00 0x04 0x00 0x00 0x00
(gdb) x /8x 0x603310
0x603310 <node5>: 0xdd 0x01 0x00 0x00 0x05 0x00 0x00 0x00
(gdb) x /8x 0x603320
0x603320 <node6>: 0xbb 0x01 0x00 0x00 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x00
列表如下:
| index | number |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0x14c |
| 2 | 0x0a8 |
| 3 | 0x39c |
| 4 | 0x2b3 |
| 5 | 0x1dd |
| 6 | 0x1bb |
| 降序排列的顺序为3->4->5->6->1->2. | |
差点忘了,代码中曾经用7减去输入的数,所以最后的答案就是 4 3 2 1 6 5 ! |
12345678910111213141516kim@MyDell:/mnt/e/Documents/C/CSAPP/bomb$ cat answer
Border relations with Canada have never been better.
1 2 4 8 16 32
3 256
0 0
IONEFG
4 3 2 1 6 5
kim@MyDell:/mnt/e/Documents/C/CSAPP/bomb$ ./bomb answer
Welcome to my fiendish little bomb. You have 6 phases with
which to blow yourself up. Have a nice day!
Phase 1 defused. How about the next one?
That's number 2. Keep going!
Halfway there!
So you got that one. Try this one.
Good work! On to the next...
Congratulations! You've defused the bomb!
拿下!
隐藏彩蛋 Link to 隐藏彩蛋
看到别人的解答发现原来bomb还有彩蛋,并没有在main函数中使用.对于我这样用gdb见招拆招的选手当然没有想到.只有把整个可执行文件反汇编才能看到,比如使用objdump重定向输出
1objdump -d bomb >> bomb.s
感受 Link to 感受
参考资料/补充学习 Link to 参考资料/补充学习
别人的解法 Link to 别人的解法
手把手教你拆解 CSAPP 的 炸弹实验室 BombLab - 知乎CSAPP:BombLab 详细解析_csapp bomblab-CSDN博客